The Impact of Climate Change on The Ocean
Source Photo: https://www.montereybayaquarium.org/stories/climate-change-a-triple-threat-for-the-ocean
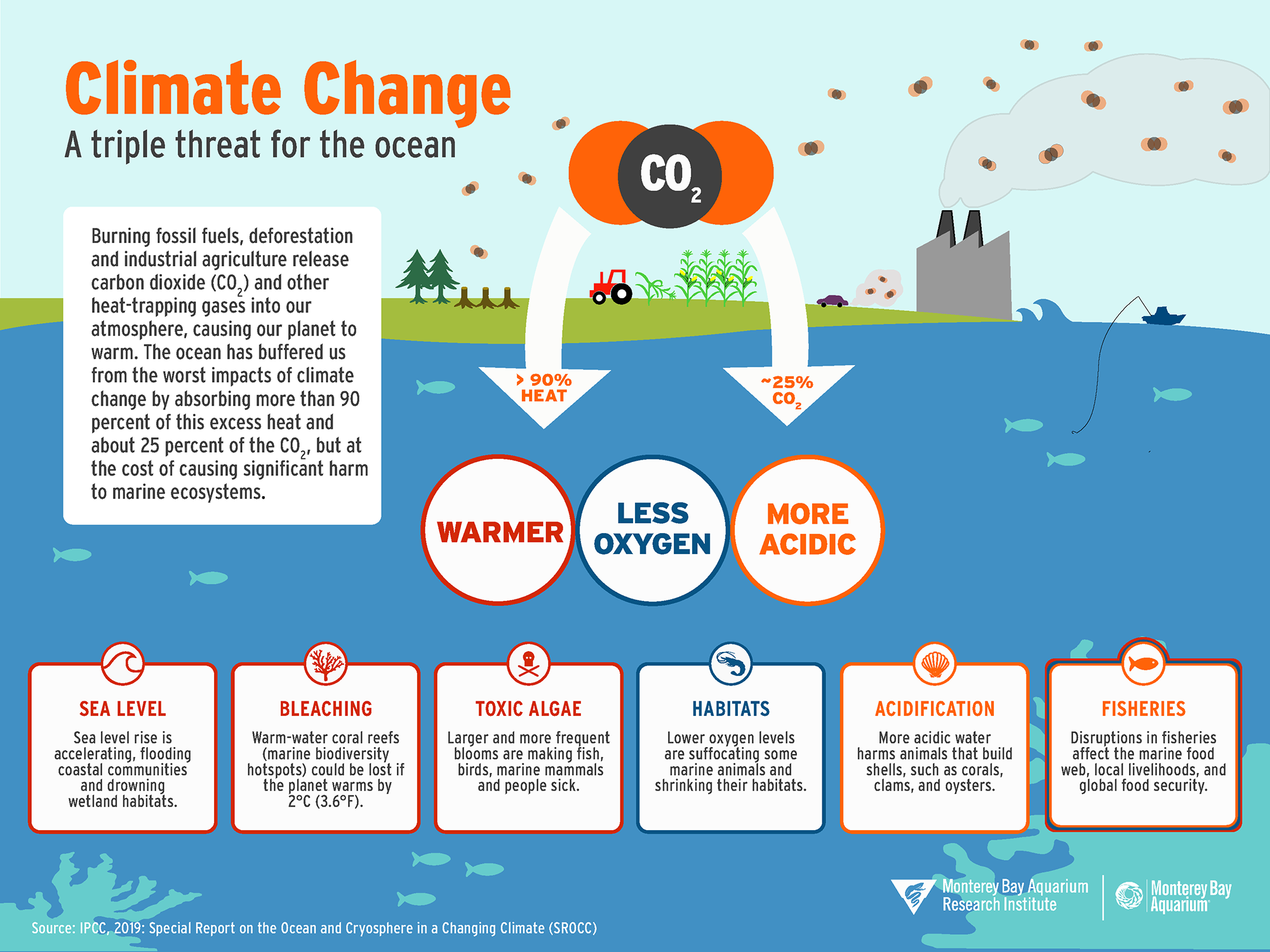
Climate change is having a significant impact on the world's oceans. The oceans absorb about 25% of the carbon dioxide (CO2) that is released into the atmosphere by human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation. This causes a phenomenon known as ocean acidification, which is the decrease in pH levels of the ocean caused by the absorption of CO2. This process makes the ocean more acidic and can have negative impacts on marine life, such as coral reefs, shellfish, and some fish species.
Another way that climate change is impacting the oceans is through sea-level rise. As the Earth's temperature increases, the polar ice caps melt, and the water in the oceans expands, causing sea levels to rise. This can have serious consequences, such as coastal flooding, erosion, and the loss of habitats for marine life. It also impacts human lives, making coastal communities more vulnerable to natural disasters and forcing people to move their homes and communities.
Warmer oceans also lead to changes in weather patterns, including more intense hurricanes and typhoons. Oceans serve as a heat sink, and as they get warmer, they can fuel more powerful storms. Also, the changes in temperature can cause changes in ocean currents and winds, leading to changes in fish migration and distribution, and disrupting fishing industries.
Climate change also causes changes in ocean temperature and salinity. It's well established that global warming has caused the ocean to warm; this causes the ocean to expand, which contributes to sea-level rise. The warming also causes changes in the distribution and movement of marine species, as well as changes in the timing of important life cycle events such as reproduction and migration. These changes have cascading effects throughout marine ecosystems.
In addition to the impacts already mentioned, climate change also causes the ocean to lose oxygen as warmer water holds less dissolved oxygen than colder water. This can also lead to the formation of dead zones, where the lack of oxygen makes it impossible for marine life to survive.
It's important to note that not all impacts of climate change on the oceans are negative. Some species may benefit from the changes, and new habitats may open up as others disappear. But the overall trend is negative, and it is important that we take action to mitigate the effects of climate change on the oceans.
In conclusion, climate change is having a significant impact on the world's oceans, causing ocean acidification, sea-level rise, changes in weather patterns, changes in ocean temperature and salinity, loss of oxygen, and dead zones. These impacts can have serious consequences for marine life, as well as for human communities that depend on the oceans. It's crucial that we take action to reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and minimize the effects of climate change on the oceans.
References:
IPCC. (2019). Climate change and the oceans. In: IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N. Weyer (eds.)]. Retrieved from https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/home/
National Ocean Service. (2021). Climate change and sea level rise. Retrieved from https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/sealevel.html
NOAA. (2021). Ocean acidification. Retrieved from https://www.noaa.gov/education/resource